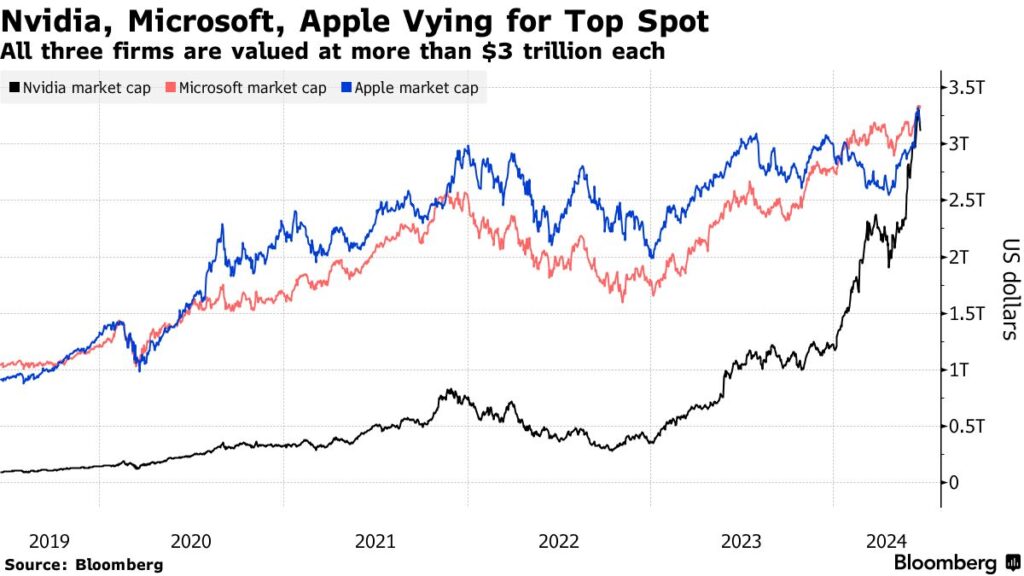
On June 18, 2024, Nvidia achieved a remarkable milestone by becoming the world’s most valuable company, with a staggering market capitalization of $3.34 trillion. This feat is nothing short of extraordinary, as Nvidia surpassed tech behemoths like Microsoft, Apple, Samsung, and Alphabet. To put this into perspective, Nvidia’s value is now so immense that it could theoretically acquire the Pokémon franchise, the highest-grossing media franchise globally, 36 times over.
The Humble Beginnings of a Tech Giant
Nvidia’s story begins in 1993, making it a relatively young player in the tech industry. The company was founded by Jensen Huang, who currently serves as the CEO, along with two other co-founders. Jensen’s career path took an unconventional route:
- Early days: Jensen worked as a waiter’s assistant at a local Denny’s diner.
- Education: He developed a passion for computer science and pursued it academically.
- Career start: Jensen landed his dream job at AMD, working as a microprocessor designer.
The pivotal moment came when Jensen identified a crucial bottleneck in PC performance. This realization led to a fateful meeting at a Denny’s diner, where Jensen and his co-founders conceived the idea for Nvidia.
The Birth of Nvidia: What’s in a Name?
The origin of Nvidia’s name is as intriguing as its rise to prominence:
- Initial documentation: Early company files were labeled “NV,” short for “next version.”
- Name search: The founders looked for words containing “NV” in that order.
- Latin inspiration: They discovered “Invidia,” the name of an ancient Roman goddess.
- Symbolism: Invidia personified envy, known for her poison tongue and green eyes.
The GPU Revolution: Nvidia’s Game-Changing Innovation
Nvidia’s ascent to tech supremacy can be traced back to a groundbreaking innovation in 1999:
- The GeForce 256: Introduced as the world’s first “Graphics Processing Unit” or GPU.
- Parallel processing: Unlike CPUs, which processed calculations sequentially, GPUs could divide tasks and process them simultaneously.
- Gaming transformation: This innovation revolutionized PC and console gaming by freeing up CPUs to focus on other aspects like in-game physics.
Beyond Gaming: Nvidia’s AI Gambit
While Nvidia’s success in the gaming market was impressive, it was their strategic bet on AI that catapulted them to unprecedented heights:
- CUDA introduction (2006): Nvidia released CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture), a software platform that unlocked the full potential of GPUs for non-graphics tasks.
- Parallel processing for all: CUDA allowed developers to harness the power of GPU cores for various applications beyond gaming.
- Industry standard: Nvidia’s GPUs became the go-to choice for video editors, financial modelers, cryptocurrency miners, and most importantly, AI researchers and developers.
Nvidia’s Ubiquity in the Tech Landscape
Nvidia’s technology has become deeply embedded in various sectors of the tech industry:
- Scientific research: Researchers use Nvidia GPUs for complex simulations, including protein folding for drug discovery.
- Autonomous vehicles: Companies like Tesla rely on Nvidia GPUs to train self-driving algorithms.
- AI tools: Popular AI services like ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini are powered by Nvidia hardware.
- Cloud computing: Amazon Web Services, which hosts approximately 30% of cloud-based internet services, utilizes Nvidia technology.
The Road to Market Dominance

Nvidia’s journey to becoming the world’s most valuable company in June 2024 was accelerated by a strategic move:
- 10:1 stock split: Nvidia divided each existing share into 10 new shares.
- Increased accessibility: This made Nvidia stocks more affordable for new investors.
- Perfect timing: The split coincided with a global surge of interest in AI investments.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its phenomenal success, Nvidia faces some challenges:
- Market corrections: After reaching the top spot, Nvidia experienced a market correction, settling into third place among the most valuable companies.
- AI sustainability concerns: Questions about the long-term sustainability of AI growth, including power consumption issues, loom on the horizon.
- Potential market bubble: Some analysts draw parallels between the AI boom and the dot-com bubble of the early 2000s.
However, Nvidia’s future still looks promising:
- AI integration: As AI becomes more pervasive, the demand for Nvidia’s technology is likely to grow.
- Digital transformation: Industries increasingly rely on digital technologies, from movie production using game engines to medical training with digital patient twins.
- Metaverse potential: If the concept of the metaverse materializes, Nvidia is well-positioned to power its underlying infrastructure.
Conclusion
Nvidia’s rise from a startup founded in a Denny’s diner to the world’s most valuable company is a testament to the power of innovation, strategic foresight, and adaptability. By pioneering the GPU and recognizing the potential of AI early on, Nvidia has positioned itself at the forefront of the digital revolution. As we move further into an AI-driven future, Nvidia’s role in shaping the technological landscape is likely to remain significant, making it a company to watch in the coming years.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
When was Nvidia founded?
Nvidia was founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang and two co-founders.
What does Nvidia’s name mean?
Nvidia’s name is derived from the Latin word “Invidia,” which means envy and is associated with an ancient Roman goddess.
What was Nvidia’s breakthrough product?
Nvidia’s breakthrough came in 1999 with the release of the GeForce 256, the world’s first Graphics Processing Unit (GPU).
How did Nvidia become involved in AI?
Nvidia entered the AI field by introducing CUDA in 2006, which allowed their GPUs to be used for non-graphics tasks, including AI computations.
What was Nvidia’s market value when it became the world’s most valuable company?
On June 18, 2024, Nvidia’s market capitalization reached $3.34 trillion, making it the world’s most valuable company at that time.
What industries rely on Nvidia’s technology?
Nvidia’s technology is used in gaming, AI research, autonomous vehicles, scientific simulations, cloud computing, and potentially the metaverse.
What challenges does Nvidia face in the future?
Nvidia faces challenges such as market volatility, concerns about AI sustainability, and potential comparisons to the dot-com bubble.